These models are only implemented for sedimentation equilibrium data.
mixed association: incompetent species are incompetent for both monomer-dimer and heterogeneous association
* log or lg means log10
* a species not participating in the association can be specified (check the 'add non-participating species' field) This is simply an additional component, perhaps an impurity, which has nothing to do with the associating molecules.
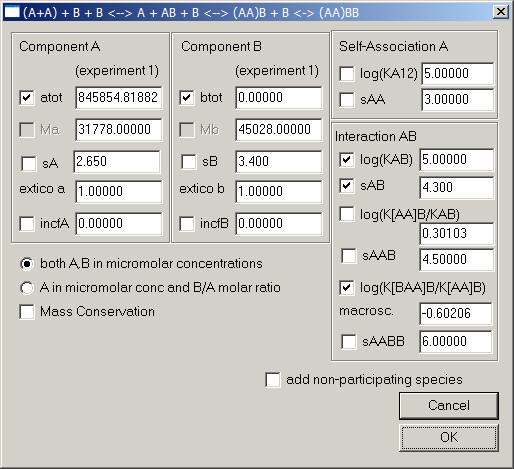
1) Monomer-Dimer A, A2 binding B, forming heterogeneous complexes AB, AAB, and BAAB


with KA12: monomer-dimer association constant (microscopic = macroscopic)
KAB: microscopic heterogeneous binding constant of B to A
aA: macroscopic cooperativity constant of K[AA]B/KAB, i.e. enhancement of AB interface through the dimerization of A. If there's no microscopic cooperativity here, the macroscopic value of this parameter is the statistical factor 2 (or log10(aA) = 0.30103).
aAM: macroscopic cooperativity constant K[BAA]B/K[AA]B, i.e. enhancement of binding of the second B to the free A of a preformed AAB complex through the presence of a prior B (either via B-B interactions, or modifications of the free protomer of A in the AAB complex) (microscopic = macroscopic). If there's no microscopic cooperativity here, the macroscopic value of this parameter is the statistical factor 1/4 (or log10(aAM) = -0.60206).
1) Monomer-dimer A, A2, and monomer-dimer B, B2, forming heterogeneous complexes AB, AAB, BBA, and BAAB
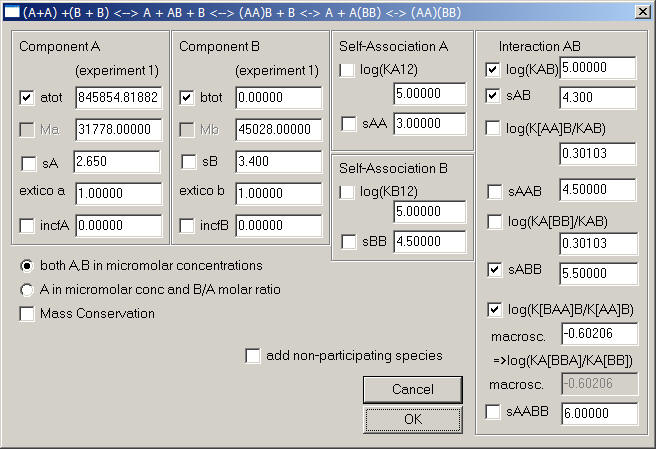

with KA12: monomer-dimer association constant of A (microscopic = macroscopic)
with KB12: monomer-dimer association constant of B (microscopic = macroscopic)
KAB: microscopic heterogeneous binding constant of B to A
aA: macroscopic cooperativity constant of K[AA]B/KAB, i.e. enhancement of AB interface through the dimerization of A. If there's no microscopic cooperativity here, the macroscopic value of this parameter is the statistical factor 2 (or log10(aA) = 0.30103).
aB: analogous to aA - macroscopic cooperativity constant of K[BB]A/KAB, i.e. enhancement of AB interface through the dimerization of B. If there's no microscopic cooperativity here, the macroscopic value of this parameter is the statistical factor 2 (or log10(aB) = 0.30103).
aAM: macroscopic cooperativity constant K[BAA]B/K[AA]B, i.e. enhancement of binding of the second B to the free A of a preformed AAB complex through the presence of a prior B (either via B-B interactions, or modifications of the free protomer of A in the AAB complex). If there's no microscopic cooperativity here, the macroscopic value of this parameter is the statistical factor 1/4 (or log10(aAM) = -0.60206).
aBM: macroscopic cooperativity constant K[BBA]A/K[BB]A, i.e. enhancement of binding of the second A to the free B of a preformed BBA complex through the presence of a prior A (either via A-A interactions, or modifications of the free protomer of B in the BBA complex). If there's no microscopic cooperativity here, the macroscopic value of this parameter is the statistical factor 1/4 (or log10(aAM) = -0.60206).
There is the relationship:
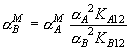
All models provide the possibility of adding an additional species that is unrelated to the reactive species.

This can be used to describe, for example, a contaminant, or IF signals from sedimenting buffer salts. The presence of such components, and their estimated molar mass and s-value may be obtained from c(s) analysis with sedfit. The purpose of the vbar in this section allows this species to be used in a flexible way in density contrast experiments (e.g. to describe the free detergent micelle).